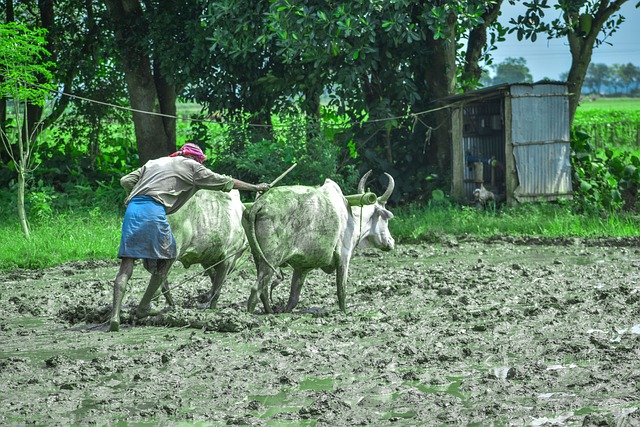

भारत का भूगोल || भारत में कृषि Geography of India || Agriculture in India
Our India is 'agrarian' country. Agriculture has an important role in our economy. According to the 2011 Indian Census, agriculture occupies about 55% of the population in India. Agriculture accounts for 17.1% of the country's gross value addition. Agriculture is a primary activity. Agriculture supports about half of India's population. Agriculture supplies us with raw materials for industries. Industries have a special place in our national income. Agriculture in India is mainly dependent on monsoon . Hence Indian agriculture is called 'Monsoon gambling' . There is a difference in the soil, climate and agricultural system of the country. Therefore, different food and non-edible crops are produced in different regions of India. India's agriculture can be classified into 3 classes based on seasons - Kharif, Rabi and Zayed .
1. खरीफ - वे फसलें जो जून से जुलाई के महीने में बोयी जाती हैं और अक्टूबर से सितंबर के महीने में काटी जाती हैं, 'खरीफ की फसलें' कहलाती हैं। उदाहरण - सोयाबीन, अरहर, धान, तिल, मूंग, उड़द, लोबिया, रागी, बाजरा, तंबाकू, कपास, मूंगफली आदि। ये वर्षा काल की फसलें कहलाती हैं। खरीफ की फसलों को दक्षिण-पश्चिम मानसून से वर्षा का जल प्राप्त होता है। इन फसलों की बुवाई के समय में अधिक तापमान तथा अधिक आद्रता की आवश्यकता पड़ती है।
1. Kharif - The crops that are sown in the months of June to July and harvested in the months of October to September are called 'Kharif crops' . Examples - Soyabean, pigeonpea, paddy, sesame, moong, urad, cowpea, ragi, millet, tobacco, cotton, groundnut etc. These are called rainy season crops. Kharif crops receive rainwater from the southwest monsoon. These crops require high temperature and high humidity at the time of sowing.
2. रबी - वे फसलें जो अक्टूबर से नवंबर के महीने में बोयी जाती हैं और अप्रैल से मई के महीने में काटी जाती है, 'रबी की फसलें' कहलाती हैं। उदाहरण - जौ, मटर, गेहूँ, चना, आलू, सरसों, अलसी, मसूर, राई आदि। ये शीतकाल की फसलें कहलाती हैं। रबी की फसलों को जल शीतकालीन पश्चिमी विक्षोभ में होने वाली वर्षा से प्राप्त होता है। इन फसलों को उगाते समय अपेक्षाकृत कम तापमान और पकने के लिए अधिक तापमान तथा दीर्घ प्रकाश काल की आवश्यकता पड़ती है।
2. Rabi - The crops that are sown in the months of October to November and reaped in the months of April to May are called 'Rabi crops' . Examples - Barley, peas, wheat, gram, potato, mustard, flaxseed, lentils, rye etc. These are called winter crops. Rabi crops get their water from winter rains in western disturbances. These crops require relatively low temperature and high temperature for ripening and long light period when growing.
3. जायद - वे फसलें जो रबी और खरीफ के मध्यवर्ती काल लगायी जाती हैं, 'जायद की फसलें' कहलाती हैं। उदाहरण - ककड़ी, तरबूज, खरबूजा, खीरा, करीला आदि। ये फसलें मार्च के महीने में बोयी जाती हैं तथा जून के महीने तक काट ली जाती हैं। ये मुख्य रूप से ग्रीष्म काल की फसलें कहलाती हैं।
3. Zayed - The crops that are planted during the inter-rabi and kharif seasons are called 'Zayed crops' . Examples - Cucumber, watermelon, melon, cucumber, curry etc. These crops are sown in the month of March and harvested till the month of June. These are mainly called summer crops.
कृषि तंत्र - यह एक प्रक्रम है, जो मुख्य रूप से 3 चरणों में संपन्न होता है। ये तीन चरण हैं - निवेश, प्रक्रिया तथा निर्गत। पहले चरण में निवेश के तौर पर मशीनरी, उर्वरक, बीज, श्रमिक तथा भौतिक निवेश जैसे - सूर्य प्रकाश, तापमान, वर्षा, मृदा, ढाल आदि को शामिल करते हैं। दूसरा चरण प्रक्रिया के रूप में होता है। इसमें जुताई, बुवाई, सिंचाई, निराई, छिड़काव तथा कटाई की जाती है। तीसरे और अंतिम चरण में निर्गतों के अंतर्गत इन दोनों चरणों से प्राप्त हुए उत्पाद जिसके अंतर्गत फसल, डेयरी उत्पाद, कुक्कुट उत्पाद होते हैं, को शामिल किया जाता है।
Agricultural system - This is a process, which is mainly completed in 3 phases. These are three steps - investment, process and output. The first phase includes machinery, fertilizers, seeds, labor and material investments such as sunlight, temperature, rainfall, soil, slope, etc. as an investment. The second step is in the form of a process. In this, plowing, sowing, irrigation, weeding, spraying and harvesting are done. Third and in the final stage, the outputs from these two stages include crops, dairy products, poultry products, under the output.
RF competition
INFOSRF.COM
संबंधित जानकारी नीचे देखें।
(Watch related information below) 👇🏻

आशा है, उपरोक्त जानकारी उपयोगी एवं महत्वपूर्ण होगी।
(I hope the above information will be useful and important. )
Thank you.
लेखक
(Writer)
infosrf.com


.jpg)




