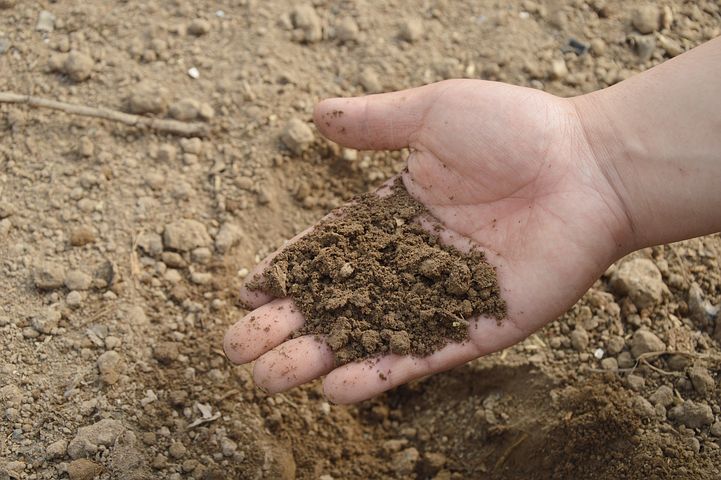

मिट्टी (मृदा) की संरचना एवं प्रकार | Soil structure and type
The upper layer of the earth is called 'soil' or 'soil' . It gives mineral salts, nutrients and water etc. as a natural source for plant growth on the earth. Soil is a mixture of fossil and mineral salts, which takes millions of years to build. There are many layers of soil in general. The top layer of it consists of small soil particles, remnants of organisms and rotting plants. The top layer of soil is very important and necessary for crop production. The second layer of soil is made of fine particles like clay. Below this is a mixture of fragmented rocks and soil, and beneath it are further disintegrated hard rocks. These can range from a few centimeters to several meters. Naturally growing plants with pH values of 6.0 to 7.0 are necessary. All plants grow on this pH value of the soil. When the pH value of the soil is high or low, it increases or decreases its acidic or alkaline nature, which is harmful for plant growth.

शैलों के अपक्षयण तथा विघटन से बने भू-पदार्थों, मलवा तथा विविध चयन सामग्रियों के मिश्रण को 'मृदा' कहा जाता है। यह भू-पर्पटी की सतह (पृथ्वी की सतह) पर विकसित होती है। मृदा के प्रमुख घटक ह्यूमस, जल, वायु तथा खनिज तत्व आदि होते हैं। इन घटकों का अनुपात (संयोजन) ही मृदा के प्रकार का निर्धारण करता है।
A mixture of soil, debris and various select materials made from weathering and dissolution of rocks is called 'soil'. It develops on the surface of the earth's surface (Earth's surface). The main components of soil are humus, water, air and mineral elements etc. The proportion (combination) of these components determines the type of soil.
इन 👇 प्रकरणों के बारे में भी जानें।
1. भारत में पशुपालन- गायों की प्रमुख नस्लें
2. भारत के मसाले एवं उनकी खेती
3. विज्ञान की शाखाएँ-जीवधारियों का नामकरण व वर्गीकरण
4. राज्यवार भारतीय फसलें
1. खनिज पदार्थ (Minerals)- About 40 to 45%
2. मृदा जल (Soil water)- About 25%
3. मृदा वायु (Soil air)- About 25%
4. ह्यूमस या कार्बनिक पदार्थ (Humus or organic matter)- 5% to 10%
5. मृदा जीव और मृदा अभिक्रिया (Soil Fauna and Soil Reaction)
मृदा परिच्छेदिका (Soil parietal)- मृदा की अलग-अलग परतों के ऊर्ध्वाधर स्तरों के सामूहिक विन्यास को 'मृदा परिच्छेदिका' या 'मृदा पार्श्विका' कहा जाता है। यह मृदा के कई संस्तरों से मिलकर निर्मित होती है। इसका प्रत्येक संस्तर अपने भौतिक और रासायनिक संगठन, मृदा संरचना और जैविक पदार्थों में एक दूसरे से भिन्न होते हैं। मृदा परिच्छेदिका को निम्नलिखित स्तरों में वर्गीकृत किया जा सकता है-
The collective configuration of the vertical levels of individual layers of the soil is called 'Soil Trap' or 'Soil Parietal'. It consists of several layers of soil. Each of its strata differs from each other in their physical and chemical organization, soil composition, and organic matter. Soil beds can be classified into the following levels-
इन 👇 प्रकरणों के बारे में भी जानें।
1. पादपों में पोषण- प्रकाश संश्लेषण
2. जैविक कृषि– कृषि की एक प्रमुख विधि
3. भारत में कृषि
4. भारत की प्रमुख जल परियोजनाएँ
Humus and organic material are abundant in this layer of soil bed. This is the ground level.

2. स्तर (Level)- A यह ऊपरी मृदा का स्तर होता है। यह स्तर मुख्य रूप से काले रंग का होता है। यह कार्बनिक पदार्थों से समृद्ध होता है। इस स्तर में खनिज पदार्थ तथा जैविक पदार्थ दोनों साथ-साथ प्राप्त होते हैं। इसको 'निक्षालन का क्षेत्र' भी कहते हैं। अधिकांश पौधों की जड़ें इसी स्तर में पाई जाती हैं।
This is the level of the upper soil. This level is predominantly black in color. It is rich in organic materials. In this stage both mineral matter and organic matter are obtained simultaneously. It is also known as 'area of depository'. The roots of most plants are found in this stage.
3. स्तर (Level)-B यह स्तर भूमि की नीचे होता है। इसमें चिकनी मृदा और गाद होती है। इसे "जल संचयन का क्षेत्र" भी कहा जाता है। यह स्तर अपने से ऊपरी स्तर के सभी निक्षालन खनिजों को संग्रहित कर लेता है। यह स्तर कैल्सिलाइट जैसे घुलनशील खनिजों से मिलकर बना होता है। इस स्तर में एल्युमिनियम, लोहा तथा अन्य जैविक मिश्रण संगृहीत होते हैं।
This level is below the ground level. It has smooth soil and silt. It is also known as "area of water harvesting". This level stores all the mineral deposits of the upper level from it. This level consists of soluble minerals such as calcillite. This level contains aluminum, iron and other organic mixtures.
4. स्तर (Level)-C यह ऋतुसुरक्षित खराब चट्टानों वाला स्तर होता है। ये चट्टानें मृदा परिच्छेदिका के सबसे नीचे अवस्थित होती हैं।
It is a layer of weather-protected erratic rocks. These rocks lie at the bottom of the soil bed.
आशा है, मृदा की संरचना के संदर्भ में जानकारी उपयोगी लगी होगी।
Hopefully, information in terms of soil structure will be found useful.
धन्यवाद
RF Temre
infosrf.com
संबंधित जानकारी नीचे देखें।
(Watch related information below) 👇🏻

आशा है, उपरोक्त जानकारी उपयोगी एवं महत्वपूर्ण होगी।
(I hope the above information will be useful and important. )
Thank you.
लेखक
(Writer)
infosrf.com


.jpg)




